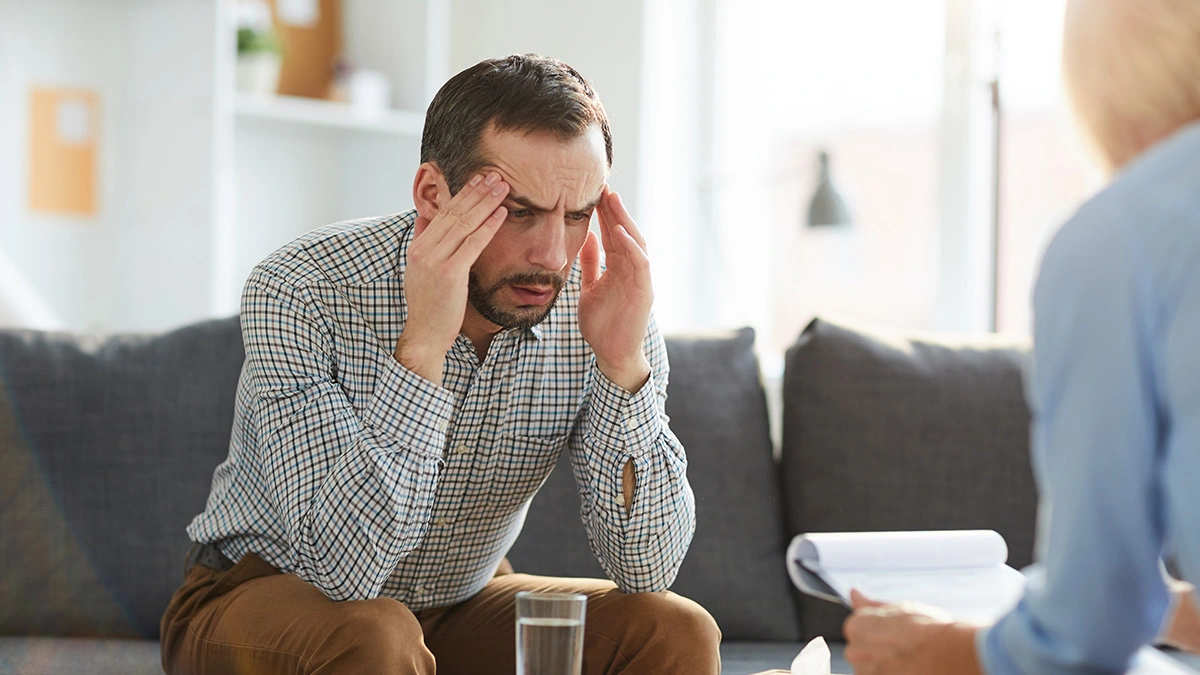
Anxiety is a mental health condition characterized by persistent feelings of fear, worry, or stress. These feelings go beyond ordinary stressors and impact daily functioning. There are many distinct types of anxiety disorders, but they all share a feeling of worry that you cannot shake. Keep reading to learn more about anxiety.
Key Takeaways
Anxiety can cause physical symptoms such as sweating, trembling, dizziness, nausea, and rapid heartbeat. Here’s what you need to know:
- Anxiety is a natural response to stress or perceived threats, triggering a heightened state of alertness.
- Excessive worry and fear can interfere with daily life and well-being.
- Identifying and addressing underlying causes is crucial for effective anxiety management.
Contact The Haven Detox-Little Rock at (501) 271-3342 for personalized mental health treatment to foster long-term wellness.

Anxiety
Anxiety is a pervasive mental health condition characterized by excessive worry, fear, and restlessness. It often manifests physically with symptoms like increased heart rate, muscle tension, and sweating.
Individuals with anxiety may experience intrusive thoughts, anticipate negative outcomes, and find it challenging to control their worries.
Signs and Symptoms of Anxiety Disorders
Anxiety disorders can occur in various ways, and people may experience a combination of physical, emotional, and behavioral symptoms. It’s important to note that everyone’s experience with anxiety can be different, and the severity of symptoms can vary.
Here are common symptoms associated with anxiety disorders:
- Excessive Worry: Persistent and overwhelming worry about everyday situations or events, even when there is no apparent reason for concern.
- Restlessness: Feeling on edge, restless, or unable to relax. Adults with anxiety may find it challenging to sit still or concentrate on tasks.
- Fatigue: Feeling exhausted, even when there is no physical exertion. Anxiety can contribute to both mental and physical fatigue.
- Muscle Tension: Experiencing muscle tension or stiffness, especially in the shoulders, neck, or jaw. This can lead to headaches or discomfort.
- Irritability: Feeling easily annoyed or irritated and having a lower tolerance for frustration. Small stressors may provoke an exaggerated emotional response.
- Sleep Disturbances: Difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or experiencing restless sleep. Some individuals may also have vivid and distressing dreams.
- Difficulty Concentrating: Trouble focusing on work or making decisions. Anxiety can lead to a racing emotional state, making it challenging to concentrate on one thing.
- Physical Symptoms: Anxiety can manifest physically, leading to symptoms such as sweating, trembling, dizziness, nausea, or a rapid heartbeat.
- Avoidance Behaviors: Individuals with anxiety may avoid certain situations or events that trigger their anxiety, leading to disruptions in daily life.
- Panic Attacks: Sudden and intense periods of fear or discomfort, often accomplished by physical symptoms such as a racing heart, shortness of breath, chest pain, or a feeling of impending doom.
- Excessive Self-Consciousness: A heightened self-awareness and fear of being judged by others. This can lead to social anxiety and avoidance of social situations.
Anxiety Disorders
Anxiety is an umbrella term for common mental health conditions that affect people in various ways. Understanding the different types of anxiety can help in recognizing and addressing these challenges.
Here are some common anxiety disorders:
Generalized Anxiety Disorder
Individuals with Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) experience continuous worry and tension, often about everyday matters. This chronic anxiety can interfere with daily life, causing restlessness and difficulty concentrating.
Panic Disorder and Panic Attacks
Panic disorder involves recurrent, unexpected panic attacks and intense periods of fear or discomfort. These attacks can lead to physical symptoms like trembling, racing heart, and shortness of breath. Panic attacks are sudden and overwhelming but usually subside within minutes.
Social Anxiety Disorder
Social anxiety disorder involves an intense fear of social situations, driven by worries about negative judgment or embarrassment. People with this disorder may avoid social interactions, impacting their relationships and daily functioning.
Specific Phobias
Specific phobias are characterized by extreme and illogical fears of specific objects or situations, such as heights, spiders, or flying. These fears can trigger intense anxiety, sometimes leading to avoidance behaviors.
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD)
OCD involves persistent, unwanted thoughts (obsessions) and repetitive behaviors or mental acts (compulsions). These rituals are performed to alleviate anxiety. For instance, someone might repeatedly check doors or wash hands excessively due to obsessive fears.
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) can develop after experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event. Signs of PTSD include flashbacks, nightmares, and severe anxiety. People with PTSD may avoid reminders of the trauma, impacting their daily lives.
Causes and Risk Factors of Anxiety
Anxiety is a complex illness, and its causes are often multifaceted. Anxiety disorders can result from a combination of biological, genetic, environmental, and psychological factors.
Here are some common risk factors and causes associated with anxiety:
Genetics and Family History
Anxiety often has a familial link. If close relatives, especially parents, have experienced anxiety, there’s an increased likelihood of its occurrence in subsequent generations.
Life Experiences and Environment
Stressful life events contribute to anxiety. Trauma, major changes, or a challenging environment, such as a demanding job or academic pressures, can significantly impact mental well-being.
Medical Factors and Physical Health
Physical health is intertwined with mental health. Conditions like thyroid disorders or chronic illnesses may elevate anxiety levels. Maintaining overall well-being is crucial for managing anxiety.
Substance Use
Substance use, like alcohol or drugs, can exacerbate anxiety. While substances may offer temporary relief, they often lead to heightened anxiety in the long run, forming a harmful cycle.
How Anxiety Affects Life
Anxiety can have a profound impact on various aspects of life, affecting individuals both mentally and physically.
Here are some common ways in which anxiety can affect different aspects of life:
Effect on Physical Health
Anxiety can take a toll on your body, triggering physical symptoms like headaches, muscle tension, and fatigue. The stress hormones released during anxious moments can impact your immune system, making you more susceptible to illnesses. Sleep disturbances are common, leading to a vicious cycle of fatigue and heightened anxiety.
Impact on Daily Life and Relationships
Anxiety can disrupt daily activities, making simple tasks seem overwhelming. Social interactions may become challenging as persistent worry and fear strain relationships. The constant need for reassurance can create a cycle of dependency, affecting both personal and professional connections.
Anxiety at the Workplace
In the workplace, anxiety may manifest as difficulty concentrating, restlessness, or a constant sense of apprehension. This can hinder productivity and job satisfaction. Fear of criticism or failure may lead to avoidance behaviors, affecting career growth. Open communication and support from colleagues and employers can be crucial in managing workplace anxiety. Anxiety’s impact extends beyond the mind, influencing physical health, daily activities, and relationships.
Recognizing these effects is the first step toward seeking support and implementing coping strategies.
Treatment and Management of Anxiety
The treatment and management of anxiety typically involve a combination of therapeutic approaches. It’s important to note that the effectiveness of different strategies can vary from person to person, and individuals may need to try various approaches to find what works best for them.
Here are some common treatment options used in the management of anxiety:
Psychotherapy
Psychotherapy, often called talk therapy, is a common and effective approach to managing anxiety. In this process, a trained therapist helps individuals understand and cope with their emotions. Through open conversations, people can explore their thoughts and fears and find practical solutions to their challenges.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is especially beneficial, teaching skills to reshape negative thought patterns.
Medication
Medications can be prescribed to alleviate anxiety symptoms. These may include anti-anxiety medicines or antidepressants. These medications work by affecting brain chemicals to restore balance.
Follow the prescribed dosage and consult a healthcare professional regularly to monitor progress and potential side effects.
Lifestyle Changes and Home Remedies
Simple changes in daily life can have a significant impact on anxiety. Regular exercise can help reduce stress hormones. Try walking in nature or practicing yoga to improve mental health. Adequate sleep is vital for mental well-being. In addition, practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing or mindfulness can promote a sense of calm.
Limiting caffeine and alcohol intake is advisable as they can exacerbate anxiety symptoms.
Coping with Anxiety
Living with anxiety can be challenging, but there are effective ways to cope with it. It’s crucial to address anxiety proactively, and several techniques can help manage it.
Relaxation Techniques
Relaxation techniques offer a practical way to ease anxiety. Simple deep-breathing exercises can be done anywhere, providing quick relief. Inhale slowly through your nose, hold for a few seconds, and exhale through your mouth. This calms the nervous system and reduces stress.
Mindfulness and Meditation
Mindfulness involves staying present in the moment without judgment. Meditation, a key aspect of mindfulness, helps center the mind. Find a quiet space, sit comfortably, and focus on your breath or a calming word. Allow thoughts to come and go without dwelling on them, fostering a sense of calm and clarity.
Physical Exercise
Engaging in regular physical exercise is a powerful way to combat feelings of anxiety. Whether it’s a brisk walk, a workout routine, or a favorite sport, exercise releases endorphins, the body’s natural mood lifters. This active approach boosts physical well-being and contributes significantly to mental health. Incorporating these techniques into daily life can make a significant difference in managing anxiety. Experiment with various methods to find what works best for you.
Remember, small, consistent steps can lead to profound improvements in your overall well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Anxiety is a mental health condition causing feelings of fear, often stemming from traumatic experiences. It can affect men, women, and children, like depression. Substance abuse may exacerbate symptoms. Consult a mental health specialist for evaluation, considering medical and physical conditions.
Clinical research aids in understanding and managing cognitive symptoms, promoting comprehensive care.
For anxiety, consult a doctor to assess medical conditions. Effective treatments, such as antidepressant medication, may be recommended. Joining support groups provides valuable information and emotional assistance to manage mental disorders.
Collaborate with healthcare providers to create a personalized treatment plan addressing your specific needs.
Common anxiety disorders include generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, specific phobias, and separation anxiety disorder. GAD involves excessive worrying, while sudden and intense fear episodes characterize panic disorder.
Social anxiety disorder involves fear of social situations, and specific phobias are intense fears of specific objects or situations. Separation anxiety disorder is often seen in children and involves fear of being away from loved ones.
Mental Wellness with The Haven Detox-Little Rock
Discover tranquility at The Haven Detox-Little Rock and conquer anxiety with our comprehensive mental health services.
Our expert therapists specialize in evidence-based therapies, offering personalized counseling to address excessive fear, boost confidence, and foster emotional well-being.