Dialectical behavioral therapy (DBT) and cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) stand out as the two prominent approaches in talk therapy. These therapies are widely practiced in the United States and cater to a broad audience seeking mental well-being.
DBT emphasizes acceptance and change, blending strategies from behavioral science. It’s particularly beneficial for individuals with intense emotions, self-destructive behaviors, and borderline personality disorder. CBT, on the other hand, concentrates on identifying and altering negative thought patterns and behaviors. It’s effective for various issues like anxiety, depression, and phobias.
Both therapies use distinct techniques, yet they aim to enhance mental health. This article helps individuals to understand their differences and how they choose the best approach to their unique needs.
Key Takeaways
The two most well-known methods used in psychological therapies are dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) and cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT). Here’s what you need to know:
- Understand the differences between DBT and CBT to pick the right one for your emotional challenges.
- Seek expert help for effective management of mental health concerns.
- Each therapy has benefits; select based on your specific needs and preferences.
The Haven Detox-Little Rock is ready to assist you in choosing the best route to greater well-being. Call us at (501) 271-3342, and let us guide you in your recovery journey.
Dialectical Behavioral Therapy: Defined
Dialectical behavioral therapy, often called DBT, is a psychological approach to help people manage their emotions, build healthier relationships, and lead a more balanced life. It’s widely used in the United States to assist individuals dealing with intense feelings, self-destructive behaviors, and mental health disorders like borderline personality disorder.
In DBT, you’ll learn practical skills to handle difficult emotions, communicate effectively, and handle conflicts. These skills are taught through group sessions and individual therapy to practice and grow. Unlike some treatments, DBT doesn’t focus on the past as much as the present and future.
Therapists using DBT help you find a balance between accepting yourself as you are and working towards positive changes. This therapy can be valuable for anyone seeking improved emotional well-being and interpersonal skills.
Basic Principles
DBT is rooted in four fundamental principles. They are mindfulness, distress tolerance, interpersonal effectiveness, and emotional regulation. These principles guide individuals to recognize their emotions without judgment, tolerate distressing situations, manage emotions effectively, and enhance communication skills.
Treatment Processes
Dialectical Behavioral Therapy (DBT) involves two essential treatment components: individual therapy and group sessions.
In individual therapy, you work one-on-one with a trained therapist who guides you in setting personal goals and developing strategies to manage your emotions, behaviors, and challenges. This private setting allows for focused attention on your unique needs and progress.
Group sessions provide an opportunity to learn and practice the four DBT principles with peers facing similar struggles. Group settings offer a supportive environment to share experiences, receive feedback, and enhance your skills in real-world scenarios.
Together, these treatment processes create a comprehensive approach that empowers individuals to navigate life’s complexities with improved emotional resilience and interpersonal effectiveness.
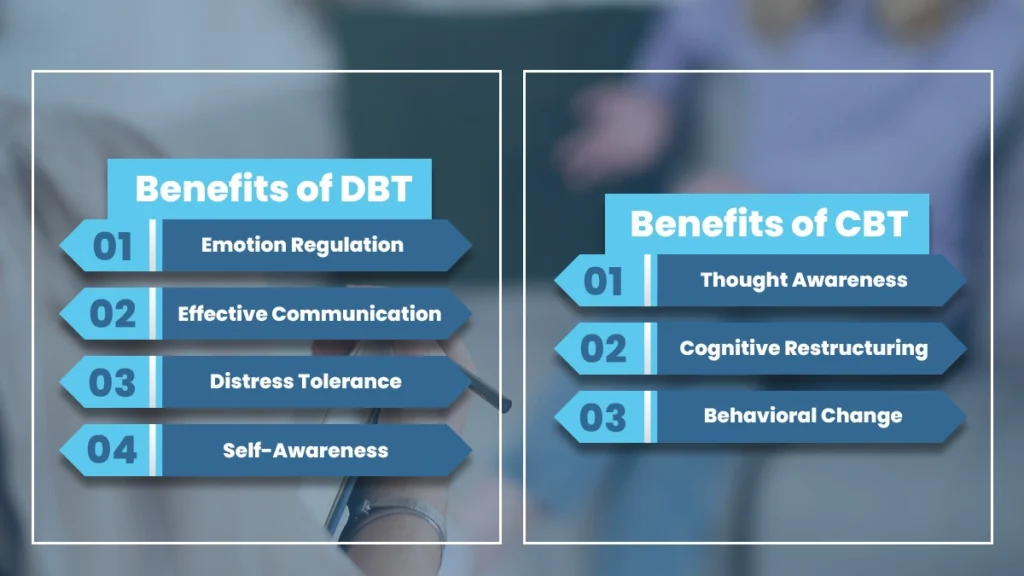
Benefits of DBT
- Emotion Regulation: DBT equips individuals with tools to manage intense emotions and prevent emotional overwhelm.
- Effective Communication: Skills learned in DBT enhance interpersonal effectiveness, leading to healthier relationships.
- Distress Tolerance: DBT teaches strategies to tolerate distressing situations without resorting to harmful behaviors.
- Self-Awareness: Mindfulness practices foster self-awareness and non-judgmental understanding of thoughts and feelings.
Limitations of DBT
- Time-Intensive: Participation requires commitment to individual sessions and group meetings, which can be time-consuming.
- Skill Application: Success depends on applying learned skills in real-life situations, which can be challenging.
- One Size Doesn’t Fit All: DBT may not address all psychological issues equally, as it’s tailored more for emotion regulation and relationships.
- Resource Availability: Access to qualified DBT therapists and programs may be limited in some areas.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy: Defined
Cognitive behavioral therapy, or CBT, is a widely used psychological approach in the United States to help individuals handle their thoughts and feelings. It’s designed to tackle various challenges like anxiety, depression, and phobias.
In CBT, a trained therapist helps you pinpoint negative thought patterns that lead to emotional distress. You learn to reframe these thoughts, replacing them with more balanced and positive ones. This shift in thinking leads to healthier emotions and behaviors.
CBT is a structured and goal-oriented therapy. It’s often a short-term treatment focusing on practical strategies for managing current issues. It empowers individuals to develop coping skills and self-awareness, enabling them to actively participate in their mental well-being.
Basic Principles
CBT is built on the concept that our thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are interconnected. It focuses on:
- Thought Awareness: Realizing negative or distorted thought patterns contributing to emotional distress.
- Cognitive Restructuring: Challenging and reframing these thoughts to promote more balanced and realistic thinking.
- Behavioral Change: Adjusting actions and reactions based on the newly cultivated perspectives.
CBT empowers individuals to participate in their healing process actively. Modifying thought patterns and behaviors aims to create lasting positive changes in emotional well-being. The collaboration between the therapist and the individual is central to the success of this approach.
Treatment Processes
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) employs structured sessions to guide individuals toward improved emotional well-being:
- Assessment: The therapist assesses the individual’s challenges and sets clear goals for treatment.
- Thought Identification: Negative thought patterns contributing to distress are recognized and discussed.
- Thought Reframing: Techniques are used to challenge and replace negative beliefs with more realistic and positive ones.
- Skill Building: Individuals learn practical strategies to manage emotions, solve problems, and cope with challenges.
- Homework: Assignments encourage the application of learned skills in real-life situations.
CBT’s collaborative and action-oriented approach equips individuals with lifelong tools to manage emotions and lead a more fulfilling life.
Benefits of CBT
- Effective for Various Issues: CBT has successfully treated anxiety, depression, phobias, and stress-related disorders.
- Structured Approach: Its organized framework provides clear strategies for individuals to implement and track progress.
- Skill Acquisition: CBT equips individuals with practical skills to manage emotions and cope with challenges.
- Short-Term Focus: Its goal-oriented nature often leads to quicker results than longer-term therapies.
Limitations of CBT
- Not Universally Effective: While helpful for many, CBT might only suit some people’s needs or preferences.
- Dependence on Participation: Success depends on an individual’s active engagement and willingness to practice learned skills.
- Focused on the Present: CBT may not delve deeply into underlying past issues contributing to present challenges.
- Ongoing Practice Required: Continuous effort is necessary to maintain and apply the skills learned during therapy.
Comparing DBT and CBT: Similarities and Notable Differences
Dialectical behavioral therapy (DBT) and cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) are two established psychological approaches that share common ground yet differ significantly in their methods and applications.
Similarities
- Evidence-Based Approaches: DBT and CBT are evidence-based therapeutic approaches extensively studied and validated through research.
- Goal-Oriented: Both therapies are designed to help individuals set specific purposes and work towards achieving them, promoting positive changes in thoughts, emotions, and behaviors.
- Structured Format: DBT and CBT sessions typically follow a structured format, providing individuals with a clear framework for addressing their challenges.
- Collaborative Therapist Relationship: Both therapies involve a collaborative relationship between the therapist and the individual, focusing on understanding the individual’s unique experiences and needs.
- Skill Building: DBT and CBT emphasize acquiring practical skills that people can use to control their emotions, improve relationships, and enhance their overall well-being.
Differences
- Focus on Acceptance: DBT places a significant emphasis on accepting oneself and emotions, aiming to find a balance between acceptance and change. CBT, on the other hand, primarily focuses on changing negative thought patterns.
- Target Audience: DBT is particularly effective for individuals with intense emotions and self-destructive behaviors, while CBT is widely applicable to various issues such as anxiety, depression, and phobias.
- Incorporation of Mindfulness: DBT integrates mindfulness techniques as a core component, while CBT generally does not emphasize mindfulness to the same extent.
- Number of Techniques: DBT incorporates four main skill sets (mindfulness, distress tolerance, emotional regulation, and interpersonal effectiveness), whereas CBT primarily focuses on cognitive restructuring and behavior change techniques.
- Therapeutic Context: DBT often involves both individual therapy and group sessions, fostering a supportive community. CBT can be organized in individual or group settings but places more emphasis on individualized sessions.
While DBT and CBT aim to improve mental well-being, their differing approaches and techniques suit distinct individuals and situations.
Through therapy sessions, individuals learn to manage symptoms, develop new skills, and enhance interpersonal relationships. Patients can navigate the complexities of mental illness and substance abuse by exploring different types of therapies.
Importance of Getting Professional Advice
Navigating mental health challenges can be complex. Seeking professional guidance is essential for several reasons:
- Expertise: Trained professionals possess the knowledge and skills to accurately assess and address your concerns.
- Customized Approach: Professionals tailor strategies to your unique needs, ensuring effective and personalized support.
- Safe Space: Therapy provides a confidential and non-judgmental environment to discuss your thoughts and emotions openly.
- Evidence-Based Techniques: Professionals use research-backed methods that have proven effective in managing various mental health issues.
- Progress Tracking: Regular sessions allow you to monitor your progress and make necessary adjustments for better outcomes.
Always remember seeking professional guidance is a proactive step toward improved mental well-being. It offers advice, tools, and insights to help you overcome challenges and lead healthier lives.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the main difference between DBT and CBT?
The primary difference lies in their focus. Dialectical behavioral therapy (DBT) emphasizes acceptance of oneself and emotions alongside the need for change, making it practical for intense emotions and self-destructive behaviors.
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) focuses on changing negative thought patterns and addressing broader issues like anxiety, depression, and phobias. Both treatments offer valuable tools for enhancing mental well-being with distinct approaches.
Is DBT or CBT more effective?
Effectiveness depends on individual needs. Dialectical behavioral therapy (DBT) excels for intense emotions, self-destructive behaviors, and borderline personality disorder.
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is versatile, aiding various issues like anxiety and depression. The choice should match your specific challenges and preferences, with both therapies having substantial evidence of helping individuals enhance their well-being.
Choose Healing With The Haven Detox-Little Rock
Are you struggling with mental health concerns and facing confusion between CBT and DBT? Find clarity and support at The Haven Detox-Little Rock.
From mental health challenges to severe addiction, we offer expert detox and residential care, guiding you toward optimal health recovery. We also employ genetic testing to let you guide personalized treatment.
Our specialists can help you decide on your optimum therapeutic route so you can recover faster and stay sober longer. Take a step towards wellness and call us at (501) 271-3342 to explore your options today.



